Views: 11
The realization of a complex work involves numerous actors: clients, financiers, general contractor, subcontractors and providers of services and materials, who operate both the client and the general contractor. The role of these figures has evolved to respond to the growing complexity and size of the projects.
Introduction
On the one hand the client, To take full control of the investment, must develop the ability to design e guide the project management system, structuring one Effective strategic planning.
On the other, Contractors must strengthen their integrated management capacity of the programs, optimizing the entire production cycle, from the design phase to the construction and test, until, In some cases, to operational management. Smaller companies, who work as subcontractors, they must optimize resources and productivity.
The Modern project management needs require a multidisciplinary approach, which must reflect in the contractual structure. A Effective strategic planning allows you to optimize processes and mitigate the risk of claims, while a well -structured contractual structure harmonizes the technical and management aspects, improving the banking of the project.
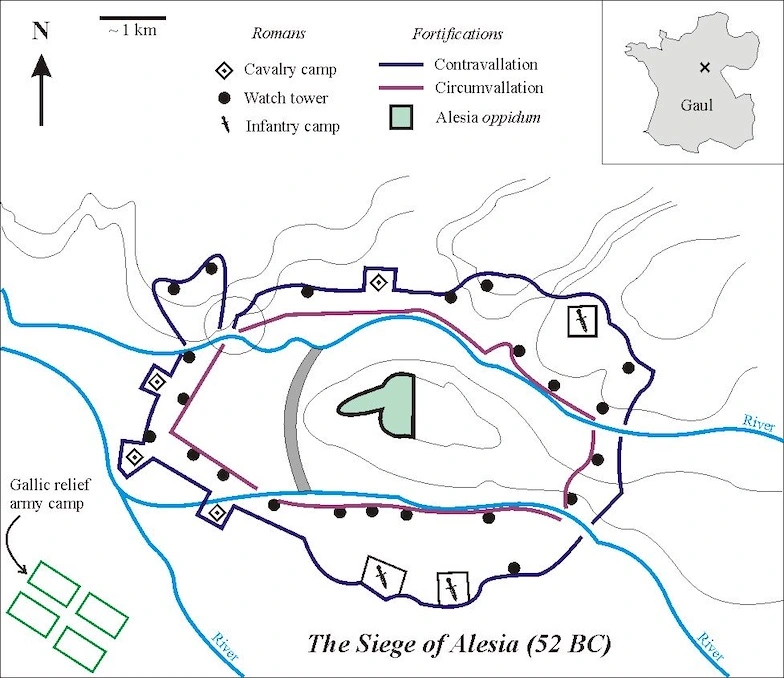
ASSIO ALESIA – Julius Caesar 52 a.C.
What is the strategic planning of the project
The success of a complex project depends on strategic choices already made in the early stages of planning. This crucial moment will condition the entire life cycle of the project, requiring effective integration between processes, Best Practice of Project Management and contractual architecture.
The Strategic planning of the project It is not limited to the definition of operational activities, but it concerns three fundamental and interconnected elements, which together determine the most suitable organizational model to carry out the project:
- Choice of the Project Delivery model: defines the method by which the project will be structured and carried out.
- Choice of the contractual model: establishes the type of contract and the responsibilities between the parties involved.
- Definition of the overall organizational model: includes the governance of the project and the forms of external assistance that is decided to acquire.
The integration of these three elements allows the client to reduce the risk, improve efficiency and guarantee the success of the initiative.
The three pillars of the strategic planning of the project
I. Choice of the Project Delivery model
The model of Project Delivery It is the first strategic decision of the client. Each model has advantages and disadvantages and must be chosen according to the characteristics of the project and its organizational structure.
Here are the main models:
- Design-Bid-Build (Dbb): traditional model in which the client develops a detailed project and then selects a contractor for execution.
- Design-Build (DB): The client entrusts both the design and the construction to a single general contractor.
- Management Oriented: Management and coordination are entrusted to specialized consultants.
Criticality: A choice not adequate to the nature and complexity of the project, Just as the limits of its organization can compromise the overall management, causing operational inefficiencies. In particular, can unbalance control in favor of the General Contractor, with repercussions on costs, Times and quality.
The model adopted directly affects the level of autonomy and the client's assistance needs. Un EPC Turnkey, for example, reduces operational involvement, but requires rigorous monitoring to ensure compliance with the contractual requirements. Vice versa, more fragmented models such as the DBB require greater commitment in the management of interfaces between the different actors. This choice impacts directly on the type of support necessary for the success of the project.
II. Choice of the contractual model
The contractual model defines the responsibilities of the parties and the regulatory framework that regulates the execution of the project. An adequate choice reduces the risk of disputes, delays and increase in costs.
Examples of contractual models:
- Lump Sum: fixed amount for the entire project, ideal when the requirements are well defined.
- Cost Plus: refund of costs incurred plus a profit margin, with greater flexibility to deal with unexpected variables.
- EPC Turnkey: The contractor manages the whole process to the turnkey delivery, reducing the client's involvement in operational activities.
Criticality: A contract not aligned with delivery strategy and the client's objectives can create difficulties in managing responsibility and compromising the contractual relationships between the parties, favoring the risks of litigation and potential negative impacts on the performance of the project.
III. Definition of the overall organizational model
The organizational model establishes the governance framework and the level of assistance that the client decides to acquire.
Key elements:
- Governance structure: definition of roles and clear responsibilities for all parties involved.
- External assistance: choice of advisor, consultants and technical support to fill any gap of internal skills.
- Control systems: integration of tools such as spring P6 for monitoring performance and analysis of deviations.
Criticality: An inadequately structured organizational model can compromise the client's ability to monitor and guide the execution of the project, reducing the effectiveness of strategic decisions.
Considerations for complex investments
In cases of great capital investments and complexity, which are strategic for the organization core business (for example, A new metro program or a new pharmaceutical production plant), The client must be adequately structured to perform a complex program/project management.
In these contexts, the most suitable choice in terms of Project Delivery Method It is the Design-Buit model, but requires specific skills and a solid organization. In other words, The client could need assistance specialized in project management, unless its organization internally provides for a department dedicated to the management of projects.
Need for a project management assistance model
The client can evaluate different forms of assistance to project management, including:
- Project Management Advisor (PMA): provides strategic advice on specific problems and activities.
- Project Control Consultant (PCC): develops and manages the project control system, monitoring costs, timing and progress.
- Project Management Consultant (PMC): assumes the complete management of the project representing the client.
- Project Management Team (PMT): integrates the internal resources to the organization with those of a consultant to fill specific skills gaps.
The choice of the assistance model depends on the complexity of the project and the client's internal capacity to manage the investment program.
The active role of the client in strategic planning
The client cannot be limited to selecting a contractor and passively wait for the project to take place.
It will be appropriate, rather, who has a proactive approach. So, will have to:
- Define a clear strategy and make sure it is applied in all stages.
- Establish the Project Governance with well -defined communication flows.
- Adopt control tools to monitor times, costs and performance and make informed decisions in real time.
Conclusion
Strategic planning is the most critical phase for the success of the project.
The integration between Project Delivery model, contractual structure and organizational structure defines the optimal structure for the client.
To reduce the risk and ensure the achievement of the objectives, An active role in management and monitoring is essential.
Acquire the skills necessary to set
Effective strategic planning!





